Many US and European firms that beforehand offshored their
industrial operations to cheaper nations equivalent to China are literally relocating
manufacturing once more to their dwelling nations.
This phenomenon, typically known as
nearshoring
or
reshoring,
has taken off massively since 2020 — first, as a consequence of COVID-19; however moreover on account of
rising geopolitical friction with China, the worldwide manufacturing hub. A
Kearney analysis reveals that 96 % of US
CEOs
intend to convey once more their manufacturing to the US, or have already taken steps
to take motion — up from 78 % in 2022.
Nonetheless, merely transferring a producing unit from China or Taiwan to Arizona or
Ohio should not be sufficient for US producers to fulfill the requires and values of US
clients. In a November 2023
survey by
American Compass and YouGov, 42 % of US clients actually really feel that
“manufacturing is important to a healthful, rising, progressive financial system” and
clamor for US-made merchandise.
The unhealthy info is that 62 % need to pay better prices to assist US
manufacturing, fairly than pay additional to combat native climate change (38 %); over
half of US adults surveyed need policymakers to focus on enhancing the US
industrial sector, fairly than bettering the setting.
The survey reveals three competing needs — revitalize left-behind communities,
improve house manufacturing, and combat native climate change — which respondents uncover
it troublesome to juggle and harmonize.
What if Western firms capitalized on the reshoring improvement throughout the US and Europe to
totally rework manufacturing price chains to have the ability to deal with their
shoppers’ three competing aspirations? Producers can receive that Holy Grail of
balancing monetary improvement, social cohesion, and environmental stewardship if
they boldly reinvent their outmoded price chains.
Limitations of worldwide price chains
In proper now’s customer-centric, collaborative and shortly altering financial system, the
standard price chain —
a set of interconnected actions to develop and convey a product to shoppers —
faces 4 most important limitations.
The linear price chain fails to work together creative ‘prosumers’
Producers view shoppers as nothing better than strolling wallets. They see patrons as
passive receivers of the price chain’s output — excluding them from actively
collaborating in R&D, manufacturing and promoting. Nonetheless, empowered by the
net, social media, digital devices equivalent to 3D printing, creative areas such
as FabLabs, and decentralized vitality
applications,
passive patrons are evolving into full of life
“prosumers” — spearheading the
Do-It-Your self (DIY) Maker
movement.
Futurist Alfin Toffler predicted
that this “prosumation” movement will velocity up all through the twenty first century and
blur the highway between manufacturing and consumption, compelling firms to
rethink their engagement with shoppers all by the price chain.
The insular price chain doesn’t favor B2B collaboration
The standard price chain focuses internally. It outlines a sequence of
associated actions carried out by a company using fully its private
property — and folks of its suppliers and companions — to point out an idea proper right into a
closing companies or merchandise for the shopper. From this angle, a mannequin’s
aggressive profit lies in its performance to optimize its private price
chain additional
successfully than rivals.
Inside the interdependent enterprise setting, nonetheless, the concept of aggressive
profit is being modified by cooperative profit. Revolutionary firms try
to collaborate with totally different firms, even rivals, to collectively create new and
larger “blue ocean” market
options which may be
advantageous for all. Because of B2B sharing
platforms,
firms in a number of sectors can proper now combine their R&D, manufacturing and
go-to-market property to co-create higher price for all stakeholders.
The static price chain doesn’t ship agility and resilience
Using lean manufacturing methods equivalent to Six
Sigma
and
Kaizen,
firms have fine-tuned their price chain to achieve effectivity helpful properties. Proper this second,
producers leverage their “lean” price chains to provide and ship their merchandise
cheaper and quicker. Nevertheless these well-oiled, static price chains lack the agility
and
resilience
needed to reply surprising market shifts.
Equally, when cataclysmic events equivalent to pandemics, wars and pure disasters strike,
many firms uncover it
troublesome
to swiftly modify their inflexible price chain processes to forestall
disruptions.
In a VUCA (dangerous, not sure, difficult, and ambiguous) world, firms ought to
collaborate with suppliers and companions to create agile and resilient price
chains
which will reply shortly to supply and demand fluctuations.
The wasteful and difficult price chain is unsustainable
From apparel and automotive to meals and vitality, every commerce price chain —
whether or not or not globally dispersed or nationally built-in — is notoriously wasteful
and unsustainable. As an illustration, from the cotton self-discipline to the shop, a pair of
jeans travels 1.5 events throughout the
planet
— which offers as a lot as 65,000 km and the associated emissions. Inside the US, current
produce travels 1,500
miles from farm
to plate. Spherical 5 % of the
electrical power
generated throughout the US is misplaced in transmission and distribution, which is
sufficient to power all seven Central American nations.
The complexity of commerce price chains makes them wasteful and unsustainable.
Faculty of Illinois researchers studied 9.5 million meals transit
routes throughout the
US. One meals journey follows “corn grown on an Illinois farm to a grain silo
in Iowa, from the place it is transported to feed cows in Kansas. After
processing, the meat merchandise then make their means once more to Illinois and onto the
cupboards of a grocery retailer in Chicago.”
Likewise, to provide a single passenger automotive — which is made up of 20,000
parts
— a carmaker ought to orchestrate a multi-tiered, worldwide price chain of roughly
8,000 suppliers. Sadly, solely 13 % of
firms
have full visibility into their multi-tiered price chain. The additional layers in a
price chain, the higher its Scope 3
emissions
(significantly upstream
ones)
— which account for as a lot as 90
% of
many firms’ complete carbon footprint.
Bottom line: firms ought to stop orchestrating hyper-global price chains which may be
inflexible, closed, and unsustainable. In its place, they need to assemble and facilitate
hyperlocal price networks which may be adaptable and sustainable, and maximize
social affect.
The rise of hyperlocal price(s) networks
A hyperlocal price group (HYLOVAN) is a dynamic, open ecosystem that
proactively features a numerous set of stakeholders inside a specific area — such
as a metropolis or county — to collaboratively develop personalised choices that
deal with native market and social requirements.
Each phrase in HYLOVAN highlights distinctive choices that make the system way more
impactful than a standard price chain:
“Hyperlocal” refers back to the reality {that a} HYLOVAN can have a geographical
differ that might probably be as restricted as a neighborhood or as in depth as an entire
metropolis — throughout the US, it would not lengthen previous the county diploma.
In order to cut back present chain payments and environmental footprint, a HYLOVAN
primarily obtains its inputs — from raw provides to workforce — from shut by
sources. A giant portion of what it produces — equivalent to companies and merchandise —
is consumed contained in the native area, although some could also be delivered to shut by
communities using eco-friendly transportation methods. Due to this, a HYLOVAN is
intrinsically frugal.
Take Vertical Harvest’s vertical farm in Jackson Hole,
Wyoming: It is three
tales tall and solely takes up 1/10 of an acre, however it is able to develop and
ship 100,000 kilos of current leafy greens year-round to native consuming locations and
groceries. On frequent, Vertical Harvest’s healthful produce solely travels 6 miles
from the farm to the customer — a rather a lot shorter distance than current meals’s
typical 1,500-mile journey throughout the US.
Vertical Harvest minimizes its carbon footprint nevertheless maximizes its social
handprint: 40 % of its employees are individuals with
disabilities.
The group is growing its worthwhile hyperlocal meals manufacturing model
to the state of Maine, the place its hydroponic greenhouse will develop yearly
over 2 million kilos of current
produce
and make use of spherical 50 underserved neighborhood members.
Equally, in early 2023, CarbonCure and
Heirloom — two startups centered on carbon
elimination and utilization, carried out a worthwhile pilot
endeavor
the place they captured CO2 from the air and saved it fully in concrete for
use in native improvement initiatives. All the price chain — the carbon-capture
unit, the concrete batch plant and improvement web sites — was situated end to complete
contained in the San Francisco Bay Area.
“Value(s)” means a HYLOVAN targets to valorize — unleash the whole price of —
bodily, pure, psychological, cultural and social belongings which have been
underused or devalued in a neighborhood area as a consequence of monetary or historic parts.
Moreover, a HYLOVAN promotes optimistic values — equivalent to equity, perception,
sustainability — inside a neighborhood by embodying them.
As an illustration, the French postal service La Poste
teamed up with SUEZ — a primary provider of spherical
environmental suppliers — to rearrange Recygo, a 3 manner partnership to assemble and
recycle office waste. Proper this second, 75,000 postal employees and SUEZ employees collect
65 tons of office waste each
day at over 23,000 web sites all through France. Recygo recycles the waste and creates
socio-economic price regionally. The waste is first sorted at a neighborhood center that
employs economically disadvantaged people after which recycled at certainly one of many 84
regional paper mills
situated all by France.
“Neighborhood” refers again to the resilient and versatile properties of a HYLOVAN,
which — in distinction with a monolithic, linear price chain — can always
adapt and
evolve
to efficiently react to shifts in its setting. A HYLOVAN can velocity up
innovation, lower risks and capitalize on new options swiftly by overtly
sharing knowledge with all members — facilitating fast and setting pleasant
coordination.
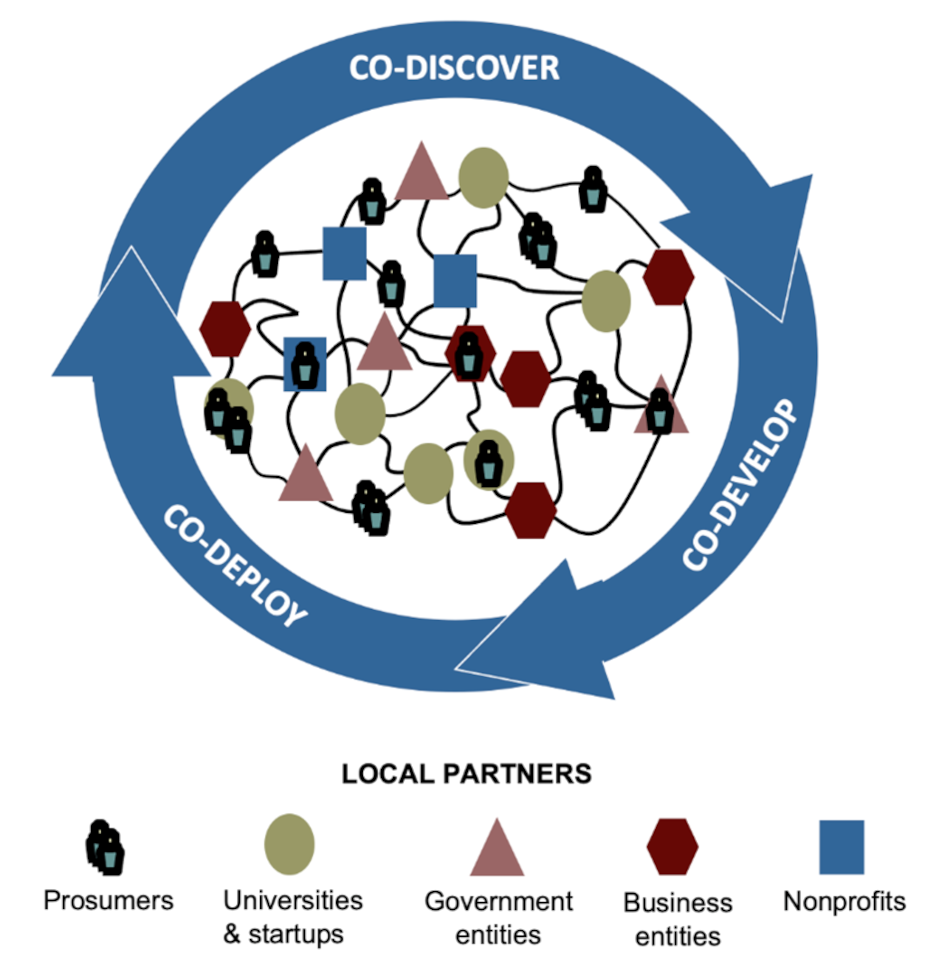 A hyperlocal price group engages numerous native stakeholders | Image credit score rating: Navi Radjou
A hyperlocal price group engages numerous native stakeholders | Image credit score rating: Navi Radjou
GRDF — France’s prime pure gasoline distributor — has
established a group of Residing
Labs
rooted deeply inside French territoires (a geographical unit similar to US
counties), with the target of repositioning native residents as the focal point of
the vitality transition. Conceptualized by MIT college students, a Residing
Lab is an open innovation ecosystem
that pulls collectively numerous neighborhood members — residents, entrepreneurs,
firms, non-profits, authorities entities — to collectively create invaluable gadgets
and suppliers that revenue and improve most people welfare.
In each neighborhood, GRDF’s Residing Lab applies agile development processes to
work together native companions to iteratively check out, be taught and deploy disruptive choices
— equivalent to the occasion of inexperienced gasoline and agroecology. These choices are
tailored to maximise sustainable price throughout the native context nevertheless could also be
replicated elsewhere. As an example, by producing biomethane
regionally using pure
waste from agriculture and meals, after which injecting it into GRDF’s distribution
group, communities receive vitality self-sufficiency, lower emissions, enhance
soil properly being, defend water property and generate employment options.
As of proper now, 547 methanization
fashions
are injecting immediately into GRDF’s distribution group. By deploying these
Residing Labs all through France, GRDF is proactively scaling out its private working
model
to permit and lead the decentralized manufacturing of renewable
gases
— which in flip, will velocity up the decarbonatization of native communities. GRDF
initiatives that by 2050, 73 % of the gasoline flowing in France’s distribution
grid might probably be inexperienced gasoline — most of which can be produced
regionally.
US and European producers that want to reshore manufacturing and reindustrialize
their nations need to first revamp their whole price chains. By establishing and
facilitating hyperlocal price networks which may be open, adaptable and deeply
rooted in communities, firms can purchase agility and resilience and maximize
sustainable native affect.
Study additional regarding the frugal financial system:
This textual content has been partially tailor-made from the creator’s upcoming e-book, The
Frugal Financial system: A Info to Establishing a Larger World with
A lot much less
(2024), printed by Wiley and Thinkers50.



